Cells make the plant and animal body. They are the smallest and most basic unit of the body. Also, cells contain many membranes and fluids inside them. Each of them has its unique role. The cell has three main parts cell-membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm.
This blog deals with the cytoplasm. You can hear learn what is the cytoplasm? Also, you can learn about the components and the role of cytoplasm. Read further to gain more knowledge.
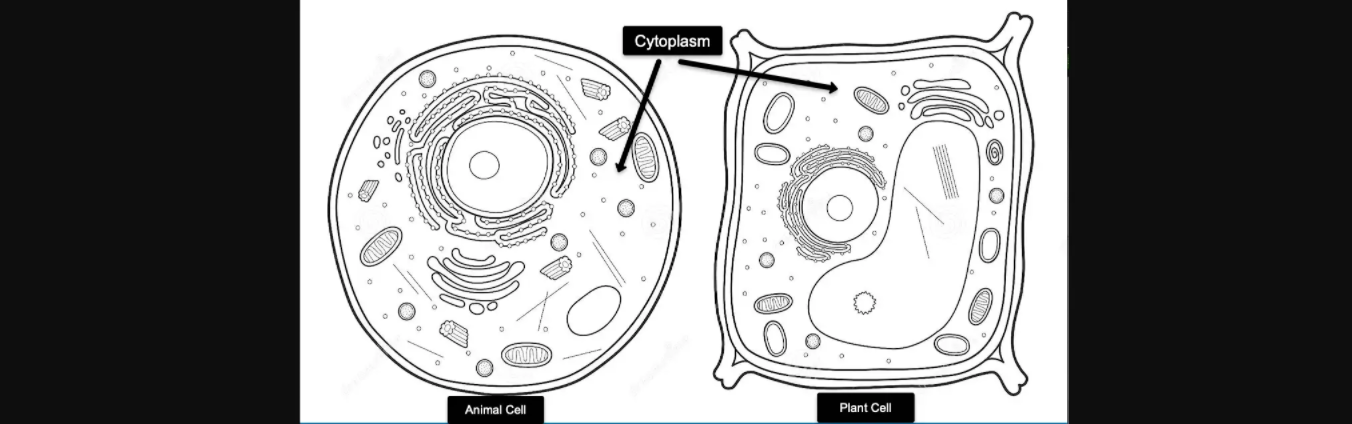
What is cytoplasm?
Cells are referred to as building blocks of the body. The cytoplasm is one of the components of cells. To begin to understand the definition of cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a thick fluid present inside each cell. It is covered by the cell membrane. The word cytoplasm is a combination of “cyto” and “plasm”. “Cyto” refers to cell and “plasm” refers to stuff.

What is cytoplasm?
The cell has many cell organelles. All the cell organelles in a eukaryotic cell float in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm also has cytosol. The difference between cytosol and cytoplasm is not difficult to understand. Some part of the cytoplasm does not have cell organelles. It is called cytosol. Scaffolds are a protein framework. It provides structure to the cell and cytoplasm.
What is cytoplasm made of?
Water is the major component of the cytoplasm. Along with water other substances are also present in the cytoplasm. These include sugars inorganic salts and organic components.

Cytoplasm in a cell
It also has proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, etc. in it. Along with this, the cytoplasm contains organelles. These organelles make the endomembrane system and cytoskeleton.
Where is the cytoplasm located?
The cytoplasm is located at different positions in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In eukaryotes a membrane-bound nucleus is present. This nuclear envelope separates the nucleus from other cell parts. So, the cytoplasm is present in between the nuclear and cell membrane.

Location of cytoplasm in a cell
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus. Then you may wonder do prokaryotes have cytoplasm? Yes, they do have cytoplasm. In prokaryotes, the cytoplasm is scattered in the entire cell. In prokaryotes, the cytoplasm contains DNA and genetic information also.
Components of Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is composed of four components. They are cytosols, cytoplasmic inclusions, and organelles. Here is a description of all three components:
Cytosol: A part of cytoplasm unoccupied by organelles. It is called cytosol. The cytosol is composed of a gelatinous fluid. All other components of the cytoplasm are suspended in the cytosol. The cytosol contains cytoskeleton filaments, organic compounds, salt, and water.
Organelles: Organelles are also called little organs. They are bound in a membrane. Organelles are present inside the cell. Each organelle has a different function. Some cellular organelles are also suspended in cytosol.
Cytoplasmic inclusions: It comprises different insoluble particles. These remain suspended in the cytosol. The membrane does not surround the cytoplasmic inclusions. Starch granules and glycogen make cytoplasmic inclusions. They store energy. There are different types of inclusions in a cell.
These were the major components of the cytoplasm.
The Cytoplasm in plants and animal cells
Both plant and animal cells have cytoplasm. But there are certain dissimilarities among the two. The cytoplasm in a plant cell is scattered. Whereas membrane-bound organelles cover the cytoplasm in animals.
Division of cytoplasm
The fusion of two haploid cells is followed by karyogamy. In karyogamy, there is a fusion of two nuclei. For karyogamy the fusion of cytoplasm and the cell membrane is necessary. You may ask how is the fusion of cytoplasm from two individuals described? It is described as plasmogamy.

The diagram shows division of cytoplasm in animal cell and plant cell
During plasmogamy the fusion of cell membrane and nucleus takes place. Now the nuclei are called pronuclei. After karyogamy division of cytoplasm takes place. Term cytokinesis is used to describe the division of cytoplasm.
Cytokinesis is a physical process. During this, the parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Before cytokinesis in animal cells meiotic and mitotic cell division occurs. These divisions separate the nuclei present in a single cell. Cytokinesis is an essential process. It ensures that each daughter cell has one nucleus.
Types of cytokinesis:
The cytoplasm in plant cells and animal cells is divided differently. There are two types of cytokinesis. They are as follows:
Plate method of cytokinesis: This type of cytokinesis occurs in plants. In this, a plate begins to form from the center of the cell. It moves towards the edges.

Plant cell divides plate method of cytokinesis
Cell furrow method: In this method, the cytoplasm of the cell is being divided by a furrow. A furrow starts to form from the edges of the cell. It continues towards the center of the cell. Finally, the cell divides into two.

Animal cell divides by cell furrow method of cytokinesis
This is how the division of the cytoplasm takes place. In both plant and animal cells cytoplasm is divided equally into daughter cells.
Functions of cytoplasm
There are many roles of cytoplasm in a cell. You need to know what is the function of the cytoplasm. Some of the uses of cytoplasm include:

Cytoplasm diagram
Most enzyme reactions and metabolic reactions occur in the cytoplasm of the cell.
It helps in cell growth and expansion.
Cytoplasm helps the organelles to remain suspended.
The cytoplasm also plays the role of buffer solution. It prevents the genetic material and cell organelles from damage.
Translation of mRNA into proteins is completed in the cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm forms cytoskeleton with the help of monomers. The cytoskeleton provides shape to the cell.
Cytoplasm ensures that every organelle stays in its place.
Cytoplasmic streaming: This plays role in photosynthesis. It positions the chloroplast near the plasma membrane. It also helps in distributing nutrients in the cell.
Cytoplasmic inheritance: In cytoplasm two organelles contain their genomic information. These are chloroplast and mitochondria. These organelles are directly inherited from the mother to the child. They have genes that are inherited outside the nucleus. In this, the cytoplasm is inherited from mother to child. This is called cytoplasmic inheritance.
There are various roles of cytoplasm in plant and animal cells. These were some common uses of cytoplasm.
Conclusion:
Cytoplasm covers 80 percent of the cell. The cytoplasm is essential in both plant and animal cells. It provides shape to the cell. And also there are many vital functions of cytoplasm in cells.