Thermodynamics is a part of physics that deals with the concept of temperature and heat and the inter-conversion of heat and other forms of energy. It may also involve other variables that are not so obvious to the human senses e.g., entropy, enthalpy, etc. they are all macroscopic variables.
The sum of the internal and pressure of the thermodynamics system is known as enthalpy. And in simple words enthalpy is the heat content of the system at constant pressure.A thermodynamics potential is a scalar quantity used to represent the state functions. It describes the equilibrium behavior of a system. Thermodynamics description involves relatively few macroscopic variables of the system, which are suggested by common sense and can be measured directly.
Significance of thermodynamics
It is used to estimate under specific conditions whether any chemical reaction occurs or not.
Used to predict the extent of reaction before reaching the equilibrium.
Used to derive important laws like the law of equilibrium.
Examples of uses:
Physical Chemistry
Power Station
Refrigeration and air conditioning
Internal engines
Aircraft, robots
Biology
Atmospheres and climate
Only a small number of principles are used in the study of thermal physics
What are the potentials in thermodynamics?
A thermodynamics potential is a scalar quantity used to represent the state functions. It describes the equilibrium behavior of a system. Internal energy is one of the main potentials that has a physical interpretation. For example, the top of Mount Everest has higher total energy due to gravity than it has at bottom. There are four fundamental functions of thermodynamics potential and these are internal energy U, enthalpy H, Helmholtz free energy F, and Gibbs free energy G.
The uses of potential thermodynamics are to measure the energy of a system in terms of different variables as it can only measure certain properties of the system. The equilibrium behavior of a system is a function of the so-called natural variables.
What is enthalpy in thermodynamics?
The sum of the product of the pressure and internal energy of a thermodynamics system is enthalpy. Enthalpy has the dimensions of the energy-like property and state function.
H=E+PV
Here, H is enthalpy, E is internal energy, P is pressure and V is volume of the system.
a) A useful new state function: when there is a change in enthalpy is negative for exothermic reactions which give off heat at the time of reaction and positive change for endothermic reactions which soak up heat from the surrounding.
b) Extensive and intensive properties: In thermodynamics, a distinction is made between two properties that are extensive and intensive. That property whose value depends on the quantity or size of matter present in the system is extensive property. Intensive properties which do not depend on the quantity or size of the matter.
c) Heat capacity: It tells how to measure heat that is transferred to a system. The heat appears as a rise in temperature of the system in case of heat taken by the system.
How do I find the enthalpy from DSC DATA?
Reaction enthalpy and reaction temperature can be determined with the help of DSC (differential scanning calorimetry). Crosslinking reactions or polymerization reactions such as reactions can be remarked as exothermal effects in DSC measurement curves.
As shown below DSC curve at a constant heating rate.
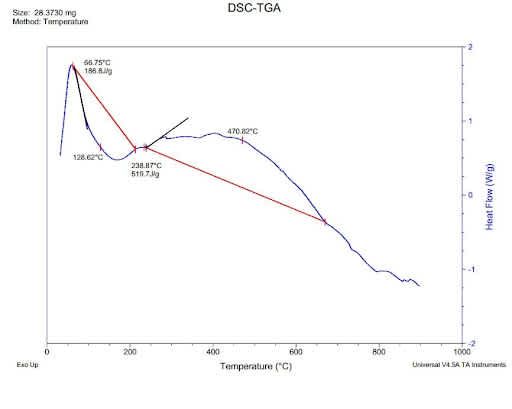
dsc-data
The change in enthalpy is caused by the reaction enthalpy, i.e. at the constant pressure; the energy conversion for a reaction is carried out. The reaction enthalpy can be obtained by DSC measurements integrating the area of reaction peak and the interpolated baselink between the beginning and end of the reaction.
Four basic thermodynamics potentials
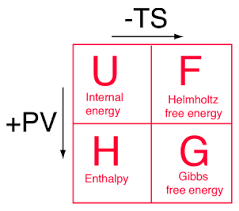
four-basic-td
There are four fundamental functions of thermodynamics potential and these are internal energy U, enthalpy H, Helmholtz free energy F, and Gibbs free energy G.
Internal energy: The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of the molecular Constitution of the system. Energy needs to create a system.It is also known as thermal energy. It depends on the size of the system or the amount of substance it includes. This energy can be stored between the atoms that make up the molecule in the chemical bonds.
Helmholtz free energy: The energy needed to create a system minus the energy from the environment.It measures the useful work obtainable from close to constant volume and pressure. The internal energy U has potential energies, S is the final entropy of the system and T is constant temperature.
F=U-TS
Enthalpy: At constant volume, heat transfer at constant volume. But in the study of the reactions, we usually have constant pressure. Internal energy minus the work needed to make it.In many measurements, the change in the energy system is at constant pressure. It simplified the description of energy transfer.
H=U+pV
Gibbs energy: G is related to entropy and enthalpy changes in the system and react
ions are generally carried at constant pressure. Total energy minus the energy we get from the environment.The change in Gibbs free energy is a very useful parameter; it can be the maximum amount obtainable from a reaction.
G=H-TS
Potential energy in thermodynamics
potential-energy-td
Potential energy is energy stored in the object because of its relative position to other objects. You have more potential energy when you stand at the top of the stairwell as compared to at the bottom, as the force of gravity pulls you down, doing work in the process. When two magnets are apart they have more potential energy than when they are close together. They will move toward each other if you let them go.
The formula of potential energy is PE=mgh
Where m is mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height, and is measured using the unit joule (j).
Types of potential energy:
a) Gravitational potential energy is stored in the object which is found at some height off the ground.
b) Elastic potential energy is found in rubber bands where the object is elastic in distorted forces.
c) Chemical potential energy is stored in the bond between atoms and molecules.
Examples of potential energy: rubber band stretching, water at the top of a waterfall, drawn bow, stretched spring
Applications of enthalpy in thermodynamics
Heat of reaction:
The enthalpy change of the system is measured as the total enthalpy of the system cannot be measured directly. The following is the equation of enthalpy change:
∆H=Hf - Hi
Where, ∆H is the enthalpy change, Hf is the final enthalpy, Hi is the initial enthalpy.
Specific enthalpy:
The uniform system of enthalpy is defined as h=H/m here m is the mass of the system. The SI is joule per kilogram.
Enthalpy changes:
That property whose value depends on the quantity or size of matter present in the system is extensive property. Intensive properties which do not depend on the quantity or size of the matter.
Physical properties of enthalpy:
Enthalpy of fusion: It completely changes the state of one mole of a substance from solid to liquid.
Enthalpy of vaporization: It completely changes the state of one mole of a substance from liquid to gas.
Enthalpy of sublimation: It completely changes the state of one mole of a substance from solid to gas.
Lattice enthalpy: One mole of the ionic compound into separated gaseous to an infinite.
Enthalpy of mixing: It is the enthalpy change upto mixing of two chemicals.
Formulas of Enthalpy
Avogadro's law formula: V=k.n
Azelaic acid formula: C9H16O4
Aspirin formula: C9H8O4
Heat of reaction: ∆H=Hf - Hi
Specific enthalpy: h=H/m
Examples of enthalpy and potential in thermodynamics
Some examples of enthalpy are:
Fire
Freezing
Melting
Boiling
The heat of solution
Evaporation
Examples of potential are: rubber band stretching, water at the top of a waterfall, drawn bow, stretched spring.
Conclusion
At last, the sum of the product of the pressure and internal energy of the thermodynamics system is the enthalpy for example fire, boiling, melting, and much more. And thermodynamics potential is a scalar used to represent the state function. For example water at the top of a waterfall. There are many chemical and physical properties of enthalpy as we understand and that is used to see the enthalpy change from solid to liquid, liquid to solid and solid to gas. In real life, this energy is used for various purposes like heating and cooling systems in our houses and buildings, motor vehicle engines that give power.